Common Causes of Back Pain
Back pain is the single largest cause of disability worldwide, including the leading cause of missed work days and loss of physical activity. 70-80% of individuals will experience back pain at some point in their life and an estimated 40-60% of the adult population will experience back pain in a given year. Back pain is less prevalent in adolescents and children compared to adults, but the incidence of back pain in children has been on the rise. Back pain has many causes and is frequently multifactorial.

Back Pain Treatment
Degenerative Disc Disease / Degenerative Joint Disease
Degenerative disc disease refers to the loss of normal disc height. Degenerative joint disease / osteoarthritis is the breakdown joint surfaces and the buildup of osteophytes (bone spurs). The vertebral disc allows for normal spacing for the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves that travel from the spinal cord to the rest of the body. Decrease in disc height and arthritic changes can lead to stenosis or narrowing the spinal cannel and neuroforamen (opening the peripheral nerves travel through) causing impingement and/or compression of the spinal cord and/or spinal nerves. Additional arthritic changes in the spine and lead to an increase in inflammation and pain. The disc have nerve endings on the outer 1/3rd of the disc. As the disc degenerate the nerve endings increase and grow inward, with more nerve endings the disc can send more pain signals know as nociception.
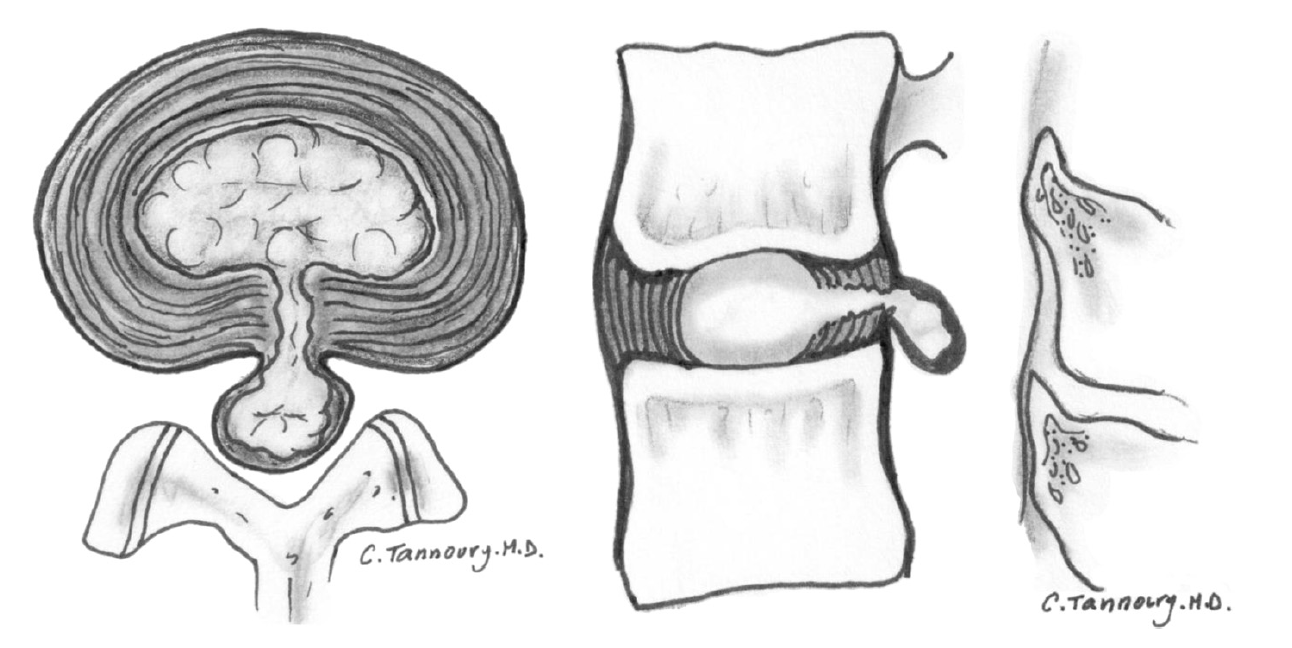
Disc Bulge / Disc Herniation
The main difference between a disc bulge and a disc herniation is a disc bulge is ‘contained’, meaning there is no rupture or tear in the disc outer layer and a disc herniation ‘not contained’ meaning the disc outer layer has ruptured. Disc bulges and herniations may or may not be symptomatic. Inflammation has been one of the main factors determining if bulge or herniation will cause symptoms. Additionally, a bulge or herniation can lead to spinal cord or nerve root compression also causing back and and/or radicular symptoms such as numbness, pain down an arm or leg, muscle weakness in a limb and/or change in reflexes.
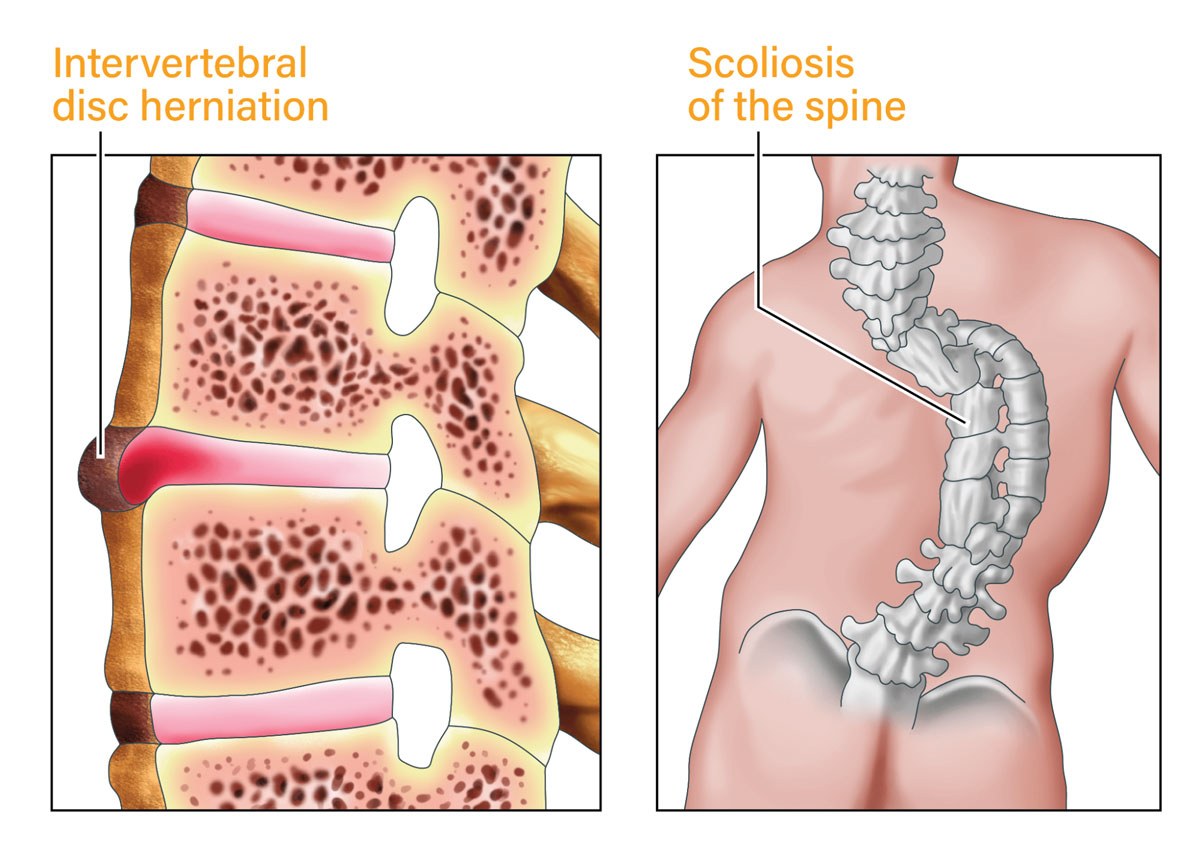
illustration of intervertebral disc herniation and scoliosis of the spine
Loss of Lumbar Lordosis
When viewed from the side (sagittal) there should be an elliptical shaped curve in the lumbar spine with the curve increasing in the lower lumbar spine. The ideal curve is about 40° however this can increase or decrease based on an individual’s anatomy. Normal curves in the spine allow for shock absorption, strength and stability. As these curves decrease it increase the load on the anterior vertebral bodies and disc increasing the prevalence in lumbar disc degeneration, bulges, herniations and spinal canal stenosis. A 2017 systematic review and meta analysis found a strong correlation with loss lumbar lordosis and back pain.
Instability
Spinal instabilities occur when there is damage to the spinal ligaments, allowing excessive motion with flexion and/or extension. Ligamentous injuries are one of the most common injures in a motor vehicle collision. Most spinal ligament injuries are know as sub-failure injuries, meaning the ligaments do not completely rupture but they are partially damaged and elongated. Once damaged ligaments never fully recovery and damaged ligament fibers are small and weaker. Spinal instabilities can lead to chronic inflammation in the joints, disc degeneration, osteoarthritis and nerve irritation.
Scoliosis
Scoliosis affects approximately 2-4% of adolescent population. Scoliosis in adolescents is most frequently idiopathic scoliosis meaning of now know cause. As individuals ages, the prevalence of scoliosis increase: 10% in adults >40 years, 38% in adults >60 years and 50% in adults >90 years. Painful scoliosis in adults may be the progression of a scoliosis that began as an adolescent and progresses in adulthood or a new scoliosis that develops in adulthood know as De Novo Scoliosis. Individuals will scoliosis have on average twice the rate of back pain when compared to individuals without scoliosis.
Loss of Sagittal Balance
The single biggest predictor of disability and decrease in health-related quality of life outcomes do to back pain is change in sagittal balance, specifically a + sagittal balance or +SVA (sagittal vertical alignment). Sagittal balance is measured by dropping a plumb line from C7 down to the superior endplate of S1. A +SVA is when the cervical spine moves anterior the sacrum and a -SVA is when the cervical spine move posterior to the sacrum. Simply put, when someone is out of balance, or when one leans or hunches forward they have likelihood of developing chronic back pain.
Back Pain Treatment
As there may be many different causes of back pain the initial steps in finding the correct and most effect treatment begins with finding the actual source of the problem. Once the main cause of the back pain is identified then the most appropriate treatment can be given.
Click here to learn causes and effective back pain treatment options.
